Commercial Integrator and Biamp recently partnered to study the commercial AV community’s thoughts on and use of sound masking technology. Over a field period of several weeks, we collected detailed responses from nearly 200 AV professionals, most of them (82%) integrators but some of them (14%) end users themselves. Here, we summarize our findings and analyze the results’ implications for integration businesses, especially those that may not yet be maximizing sound masking as a profit center.
Sound Masking Increasingly Well Understood
As regards familiarity with sound masking, our survey respondents divided quite evenly between those who are highly knowledgeable about the technology and those with only base-level knowledge. Looking at the numbers, 47% of integrators answered “Extremely familiar” or “Very familiar,” whereas 45% answered “Moderately familiar” or “Somewhat familiar.” Only 8% described themselves as “Not at all familiar.” This is an indicator that industry leaders like Biamp, known for its Cambridge Qt X Series sound masking solution, have been successful in educating the market.
Our next question focused on the benefits of sound masking: in particular, its ability to increase workplace productivity. Some 70% of respondents describe sound masking as either “Moderately important” or “Very important” to improving productivity, and another 18% describe it as “Extremely important.” This is a clear recognition of the fact that sound masking provides improved privacy in corporate settings, reduces in-office distractions and more. This underlying grasp of the value proposition suggests that integrator respondents are likely already leveraging this technology to enhance workplace outcomes and that their clients are likewise demanding sound masking implementation. We’ll put that theory to the test in our next question.
Sound Masking Study Examines Integrators’ Perspective
For one segment of the study, we limited our purview only to integrators, consultants and other channel members. The first question we asked this group was whether their clients typically use any form of sound masking. Aligning with expectations, a 44% plurality answered “Yes,” indicating that sound masking has become fundamental to their clients’ deployments. Another 40% answered “Varies greatly among clients,” reflecting the broad portfolio of verticals in which they work, not all of which equally benefit from sound masking. Only 16% of responding integrators said sound masking is not typical in their clients’ deployments. This buttresses our belief that not only integrators but also their clients now recognize sound masking’s benefits.
Next, we asked channel members to name several factors that motivate their clients to implement sound masking. Here, the dominant answer was clear: Some 82% of respondents answered “Improve privacy” as a top factor. That underlines why sound masking not only serves corporate settings but also benefits healthcare environments, government facilities and anyplace else where personally identifiable information (PII) or confidential secrets must be protected. In addition, 64% of survey takers cited “Reduce distractions” as a primary factor, with another 46% saying “Increase productivity.” Other answer choices, such as “Compliance with standards,” attracted comparatively less integrator response (22%).
When we asked channel members to name several important features they weigh when recommending a sound masking system to a client, we found that integrators consider numerous interrelated factors. The two biggest were “Cost-effectiveness” (62%) and “Ease of installation” (57%), which helps prove integrators’ client-centric thinking when making recommendations. For our survey takers, the next three answer options were bunched close together: “Sound quality” (48%), “Scalability” (45%) and “Customizability” (43%). It’s notable that every feature option that we provided attracted significant response. This illustrates integrators and consultants’ mindfulness when evaluating sound masking solutions from industry leaders like Biamp and others.
Client Control and Management
We asked integrator respondents to choose any options that align with how their clients prefer to control/manage their sound masking systems. One answer stood out from the pack, with some 65% of survey takers answering “Automated settings.” This reflects another nod to simplicity for the client and the proverbial “easy button” that everyone seems to want. Another one-third indicated “Manual controls,” perhaps hinting at a desire among some clients to fine-tune their sound masking throughout the day or week as different circumstances present themselves. Further back was “Remote control via app,” which attracted only 27% of respondents, perhaps indicating some integrators’ belief that the app-centric interfaces many end users prefer for other technologies are less compelling for sound masking.
Instructing integrators to mark any answer that applies, we asked our survey respondents to identify who in the client organization typically makes the decision to implement sound masking. Here, once again, we find responses spread across numerous answers. Fully half of survey takers said “Senior management” has a seat at the table, with another 49% selecting “Facilities management.” In addition, “IT department” attracted meaningful response at 29%, whereas other answer options — “Human resources” (14%) and “Other” (6%) — were much further back.
Sound Masking Study Offers Views from End Users
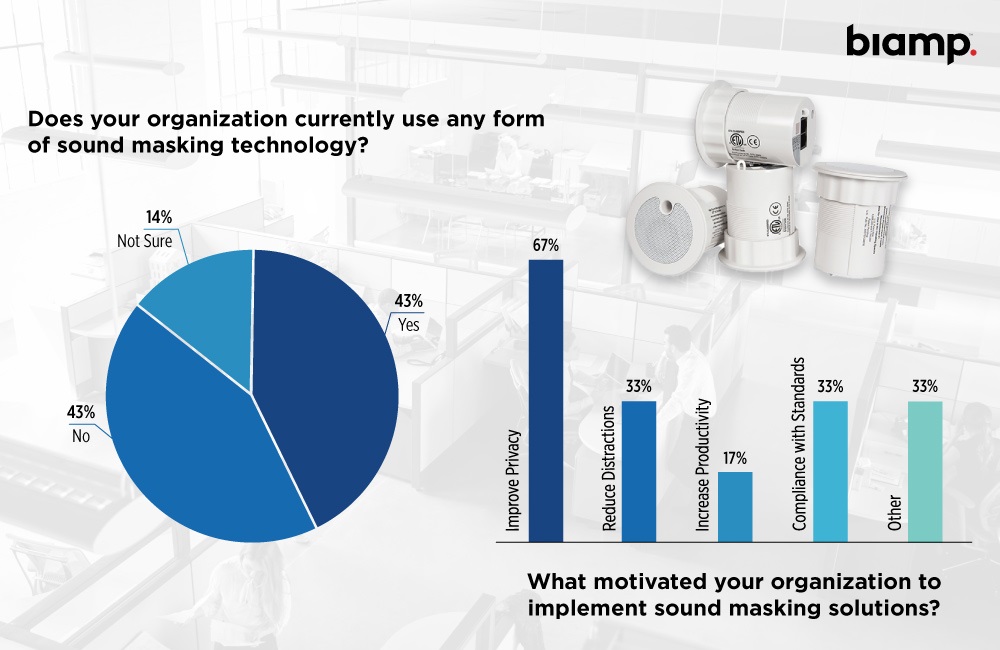
Next, we asked questions just to end-user survey respondents to understand how, if at all, their views differ from the channel partners they work with. On the baseline question of whether their organization uses any form of sound masking, 58% answered “Yes,” another 29% said “No” and 13% claimed to be unaware of their organization’s sound masking usage. This aligns pretty well with our earlier-discussed integrator responses, where a small plurality indicated sound masking had become fundamental to their clients’ deployments and where another significant percentage said considerable variation existed from client to client. The conclusion here is clear: Most end-user organizations — especially those in key verticals like corporate, healthcare and government — are leveraging sound masking to improve experiences.
We asked end users to identify several motivators for their organization to implement sound masking, and their answers aligned well with integrators’ own assessment, albeit with a caveat. End users said “Improve privacy” was an important motivator, with that answer attracting 79% response. Another 50% reported “Reduce distractions” as a motivating factor. So, the first-place answer and second-place answer mirror integrators’ survey responses. The difference arises with “Compliance with standards,” which ties for third place as a motivator for end users, attracting 29% response and equaling “Increase productivity” as a sound masking motivator. Given that end-user organizations — for example, healthcare providers — must adhere to regulations protecting patient privacy (e.g., HIPAA) and can be held to account if they do not, it’s perhaps not surprising that these survey takers are especially attuned to standards compliance.
When we asked end users to identify several features that they consider most important in sound masking systems, their answers almost perfectly reflected integrators’ feature prioritization. “Cost-effectiveness” (72%) was the clear first choice, with “Ease of installation” (64%) coming in second. The only difference here was that end users assigned even more importance to those virtues — economy and simplicity — than integrators did. For end users, “Scalability” (56%) exceeded both “Sound quality” (40%) and “Customizability” (40%) in importance. This perhaps illustrates a desire among enterprise organizations — for example, Fortune 500 businesses — to acquire a sound masking solution that can be scaled across buildings and campuses for a uniform, predictable experience.
End-User Preferences for Control and Management
We asked end users how they prefer to control/manage their sound masking systems and found the same general order that integrators had provided, but it was a much closer contest. Given the chance to choose as many options as they wished, 60% of end users selected “Automated settings,” while 44% chose “Manual Controls” and 36% selected “Remote control via app.” As readers will recall, the gulf between preferring automated settings and preferring app-based control was much larger among integrators/consultants surveyed: a whopping 38-percentage-point gap. Arguably, this demonstrates end users’ desire to leverage the interface that all of us use every day to control our music and room settings — our smartphone or tablet — to also control our sound masking technology.
We asked end users which person or group within their organization makes the decision to implement sound masking. We found responses clustered in a fairly tight range. Some 44% indicated “Facilities management” has a decision-making role; another 40% said “Senior management” has the reins. Some 28% answered “IT department” as a decision influencer, whereas only 4% cited “Human resources” as a factor in implementing sound masking. Interestingly, 24% indicated “Other” as the decision-maker, with one write-in response indicating there ought to have been an option for “AV Department.” Another write-in was for “Capital Planning & Construction.”
Sound Masking Study Finding: An Increasingly Important Solution
Commercial Integrator and Biamp initiated this study of the industry because, together, we believe that sound masking is a vital solution across numerous key verticals as well as an under-appreciated profit center for commercial AV businesses. To put our belief to the test, we asked our full pool of nearly 200 survey respondents one more question: Do you believe the importance of sound masking in commercial spaces will increase, decrease, or stay the same in the next five years? Nearly 56% of respondents answered “Increase,” expressing a belief that ever more clients will implement sound masking to deliver greater privacy, reduce distractions, increase productivity and ensure regulatory compliance. Another 30% of survey takers thought sound masking would remain just as important in the coming five years as it is now. A mere 6% said “Decrease,” indicating just how few members of the industry community think sound masking is a shrinking segment. Another 8% answered “Not sure,” which probably indicates nothing more than the unpredictability of not only AV trends but also societal conditions. (Who predicted the COVID-19 pandemic before it was already upon us?)
If you’d like to learn more about sound masking, its implementation and solutions from industry-leading providers like Biamp, go to Biamp.com/solutions/applications/soundmasking. The company can provide case studies, best-practice guides, product updates and more, while also recommending tutorials that will increase your understanding of sound masking and its application.